Note
Development has started in JS and Python, but we are still ironing out the wrinkles.
Hub & Scope Refactoring
Historically Sentry's SDKs implemented the Hubs and Scopes models, a major defining aspect of the Unified API. This introduced a lot of complexity in a user facing manner, allowed more room for error from the user as well as SDK maintainers. Since looking at adopting OpenTelemetry "packages", to replace or in addition to, our existing performance packages in SDKs, there is a forcing factor. Sentry's model being different to OpenTelemetry's prevents us from supporting OpenTelemetry.
A) Why Are We Doing This?
There are two reasons we are doing this:
- Being compatible with OpenTelemetry (OTel) performance data.
- Make Sentry performance instrumentation easier to understand and get right.
Being Compatible to OpenTelemetry
What Sentry calls a Scope is called Context in OTel. Contexts in OTel are immutable and thus whenever a context is mutated in OTel a new context is created (forked from the currently active scope).
Whenever a new span is created in Otel a new context is forked. This leads to a lot of nested contexts and the Sentry scopes should be able to reproduce this.
This is necessary because the Sentry SDKs should be able to capture all spans from OTel with the correct data from the correct context applied to them before sending them to Sentry.
Make Sentry Performance Instrumentation Easier
Hubs and scopes is a complicated system, that can easily be misused (also see here). It requires us to create new hubs which in turn breaks breadcrumbs and other features. For the future we want to have one consistent system, that is easy to understand and use.
B) What Is the Outcome of the Refactoring?
- The SDKs model of Scope forking is aligned with the one from OTel. Paving the way for making it possble to use OTel tooling for performance monitoring and still see their data in Sentry. (And Sentry error events are still connected to the spans captured by OTel).
- The new Scopes API is implemented in the API and can be used.
- The old
Hubbased API still works as expected for backwards compatibility. After a transition phase theHubwill be removed in a major update of the SDK.
Note
This is why we started this journey with an RFC.
C) The New Concepts
The Hub will be removed and only the Scope, the Client, and the Transport of the Unified API will remain.
Transport
The Transport is not touched. It will not change.
Client
The Client stays the same. The only difference will be that there is always a client available. More on that later.
Before Sentry.init is invoked, there's a NoOpClient on global scope which is replaced by an actual client on Sentry.init. Users may bind a different client to either of the three scopes.
Scope
This is where the most work needs to be done. The Scope will evolve and take over some functionality of the Hub.
The scope now comes in three flavors:
- Global Scope
- Isolation Scope
- Current Scope
No matter the flavor of the scope, you still can add data (like tags, breadcrumbs, attachments, user, profile, ..) to it like before. The scope still holds the propagation context containing tracing information.
The difference is in how the scope data is applied to events.
Global Scope
This is a simple global variable that is the same for the whole execution of the software. Data applied to this scope will end up in all events sent from the software. So the same for all users, threads, async tasks, everything.
This scope is probably only used for process-wide data like the release.
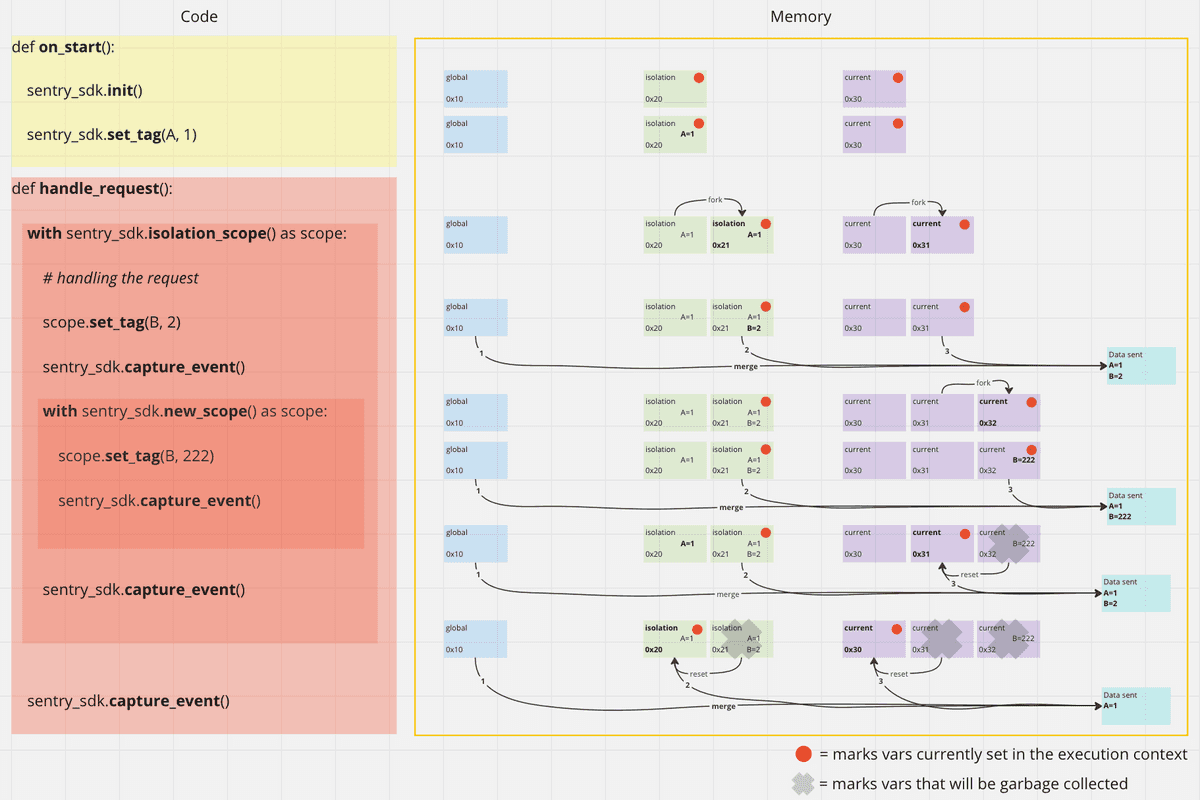
Isolation Scope
This scope holds data only applicable to the current request (on a server), tab (in a browser), or user (on a mobile). The top-level APIs that manipulate data (like sentry_sdk.set_tag(), sentry_sdk.set_context() etc) write to the isolation scope (at least once the migration phase is over, see "Backwards Compatibility").
The isolation scope is stored in a context variable, thread local, async local, or something similar (depending on the platform). It may also be stored on OTel Context so we can rely on OTels Context propagation once SDKs implement POTEL.
The isolation scope is forked by our integrations, end users should not need to think about isolation scopes or forking of one (See diagram below.).
SDKs should not fork isolation scope more than necessary as otherwise we'd bring back the problem that isolation scopes are meant to solve.
Current Scope
This scope holds data for the currently active span. Whenever a new span is started the current scope of the parent span is forked (read: duplicated) giving the new span all the data from the parent span and making it possible to add/manipulate data that is just applied to the new span (see also "Copy-on-write").
Changing the original scope after forking does not modify the forked scope.
The current scope is stored in a context variable, thread local, async local, or something similar (depending on the platform). It may also be stored on OTel Context so we can rely on OTels Context propagation once SDKs implement POTEL.
The current scope can be forked by the end user. Either explicitly (e.g. using Sentry.withScope() or implicitly by starting a new span. (See diagram below.)
Copy-on-write
Getting rid of hubs also implies a soft copy-on-write.
In our current system with hubs and scopes, Scope is always mutable and what makes it somewhat immutable is pushing/popping scopes as well as creating new hubs. This however has to be done manually.
If an async operation is started halfway in between handling a request, a new hub clone has to be created to achieve copy-on-write. In case we don't create a new hub clone, popping a Scope also affects the original execution, leading to lost data or worst case exceptions.
After merging hubs and scopes, scopes can be forked at any time and a user no longer has to take care of it, as it should automatically do the right thing. With this new system, the async execution can manipulate scope without affecting other execution.
This soft copy-on-write relies on Scope being forked in certain cases:
withScopeand similar API wraps the callback in a forkedScopethat'll be cleaned up by the SDK after the callback is finished- we also have to fork, when OTel does, however there's some grey area here at the moment
- it depends on what API is available in the OTel implementation relevant for each SDK
- in some cases, we may only be able to intercept
Contextstorage, i.e. when an already forkedContextis being stored, e.g. in a ThreadLocal variable. - in some cases we can intercept
Contextforking, i.e. when a mutated copy of aContextis created - in some cases it might be necessary to have a mix of both, since not all auto instrumentation and user instrumentation go through a single place in the same way. e.g. in Java SDK we're sometimes handed a
Contextwith some properties already set into ourContextStoragewhere we can then wrap it and intercept future forks of thatContext - {open question} do we need to fork every time OTel
Contextcopied or only when a new OTel span is set
While it's still possible to misuse, this is a sort of soft copy-on-write that should protect most users.
D) Backwards compatibility
Migrating from Hubs and Scopes to Scopes Only
There has to be some period of time, where users can keep using the old API. We do not want a big bang change, where we leave behind users who can't easily upgrade. This bears the risk of having to support old versions of the SDK. This means we shouldn't have a major version A of an SDK that has hubs and then the next version that has them merged no longer supports hubs. There has to be a migration phase for our users.
For the migration phase we can have top level static API (like Sentry.setTag()) write to both current and isolation scope. In a later major version we can then change this to only write to isolation scope. Hub API should be shimmed and redirect to scopes.
For most use cases writing to isolation scope should be what we want. For other use cases users should mostly be using withScope() already where they use the Scope passed into the callback instead of static API. We're deprecating configureScope to let users know they should reevaluate what scope they want to write to. Users can then get the scope they need and call e.g. setTag on that Scope. There might be some cases where we change behaviour but the damage should be contained to e.g. an incoming server request.
We should make it very clear in the changelog that top level API only writes to isolation scope, after we change it.
E) Implementation Details
We will merge the functionality of the Hub and the Scope of the Unified API into the Scope and we will remove the Hub. We will add some new APIs that make it easier for the user to do custom instrumentation. We will update our auto instrumentation to fork a scope whenever a new span is created. This aligns us with what OTel does.
TODO: add where the propagation context is stored and applied, add how tracing without performance works, where spans/transactions live and other problems we discovered and solved in implementing this in the first two SDKs.
How Is Scope Data Applied to Events?
Data from the different scope flavors is merged before it is applied to the event.
This is done in the following order:
- take the data from the global scope
- merge in the data from the isolation scope
- merge in the data from the current scope
- optional: merge in given additional data
- apply the merged scope to the event
See the RFC for a code example.
See the diagram below for an illustration of how scope data is applied to events.
What Does the New API Look Like?
There are now two new APIs for forking the current scope or forking the isolation scope (and at the same time the current scope.) They should be called withIsolationScope(callback) and withScope(callback) or something similar.
This image illustrates the behavior of these new APIs and how scope data is applied to scopes:
For a zoomable version visit the Miro Board
Here's how the new APIs roughly map to the old-style APIs. In case of configure_scope and push_scope it's not clear-cut whether to use the current or the isolation scope. The choice essentially depends on how long/for which context the changed/forked scope should be active.
| Old API | New API | Note |
|---|---|---|
hub = Hub(Hub.current) (hub clone) | with isolation_scope() as scope | |
with configure_scope() as scope | scope = Scope.get_isolation_scope() | Should affect the whole transaction (one request/response cycle, one execution of a task, etc.). |
scope = Scope.get_current_scope() | Should affect the whole span or a part of code isolated via a forked current scope with new_scope. | |
with push_scope() as scope | with isolation_scope() as scope | We're starting a new transaction-worthy unit (request/response cycle, etc.). |
with new_scope() as scope | Should affect a localized part of code, e.g. if the user wants to add specific data to a specific event. |
Thing we found while implementing
- We need to have good defaults for forking behaviours so our customers don't have to think about it. There's integrations, where forking only current scope or forking both isolation and current scope makes sense. We should find a good default that works for most customers.
- No longer having a stack of scopes means you should no longer call methods on actual Scopes (used to be Hub) references. When a fork is happening and e.g.
setTagis invoked on the previousScopesreference, the data won't be visible inside the forked scopes. This used to work but no longer does. - We now have to create global scope very early when the customer hasn't had a chance to specify their options. We use default options for things like breadcrumb limit etc. until
Sentry.initwhere we replace the options used on global scope. This also means we're now creating multiple instances ofSentryOptions, so we need to lazily create things like executors/threads etc. that are costly. - If another SDK builds on top of the SDK that's being changed, there may have to be some sort of CombinedScopeView that merges the scopes into one for synching. This should no longer be needed as soon as the other SDK also supports different scope types.
- If insertion order matters for data we now need some way of sorting when merging data, e.g. to send out an event. For breadcrumbs, we want to send them in insertion order which means we somehow have to keep track of when a breadcrumb was added. When merging data we then sort them and afterwards apply the breadcrumb limit again. A similar problem exists for event processors on scope as well which should also be executed in insertion order.
- It feels like there should be some easy to use API for forking isolation scope, starting/continuing a trace (and transaction) from incoming headers/metadata which currently doesn't exist.
- We decided to not deprecate/remove configureScope for Java SDK as it makes it harder for customers to hold a reference to a scope (which they shouldn't). It now has an overload that allows passing in a scope type (global, isolation, current, combined). We have a default scope we write to for the old overload. We do not want to default to combined/merged scope since that would mean you can manipulate a scope you wouldn't expect, e.g. when using
withScope. - For Java SDK we also keep
pushScopearound and addedpushIsolationScope. We deprecatedpopScopeas users should now callcloseon a lifecycle token we hand back in the push methods. The token can also be used as an automaitcally closed resource in atryblock.
F) Use OTel for Performance Instrumentation (POtel)
For more information like the goals (and non-goals) see this GitHub Issue:
https://github.com/getsentry/team-sdks/issues/4
Isolation Scope
Without an isolation scope, writing to the current Scope can lead to unexpected results. Writes can go to a scope that's never applied the way a user would expect. While this is already a problem today, it is exaggerated by moving over to OTel, as OTel auto instrumentation can do lots of context forking, leading to deeply nested scopes. Some hooks are automatically wrapped in a new span by OTel, causing it to also have a separate Scope, so the outer Scope can't be manipulated.
With isolation scope, we have a place where e.g. hooks can write to that should affect e.g. the whole request.
When isolation scope is forked, the SDK should also fork current scope at the same time. Otherwise users would have to e.g. call both withScope and withIsolationScope leading to less readable code.
Implementation Details
OTel Context
OTel stores spans as well as other information in a Context and takes care of propagating this Context through libraries and threads. We want to rely on this propagation as it allows us to not worry about propagation, instead we just store our scopes in Context and trust OTel to propagate it correctly.
Can't we simply propagate our Scopes ourselves and ignore OTEL Context?
If we didn't want to rely on OTels Context propagation, we'd have to provide a counterpart for every OTel propagation mechanism. We would no longer be able to just rely on OTel for instrumentations but have to mirror some of what they do. This would also have to be kept up to date. Whenever OTel changes something about how they propagate Context we'd have to adapt as well. Keeping Context and Scopes in sync would be hard and possibly also hard to detect. Version compatibility between Sentry and OTel could also become difficult.
Examples of where we had to provide our own propagation before POTel:
- Reactive libraries (current Sentry implementation vs OTEL)
- Executor libraries where you can schedule a task to be run on another thread (current Sentry implementation)
Restoring Context
OTel has a lifecycle token called Scope which they hand back from context.makeCurrent() and span.makeCurrent(). The user is expected to call .close() on this token. However if any of the inner Scope objects is not closed, parent Scope objects do not restore the previous Context.
This is problematic since we fork Scopes and make them the current one (which implies forking Context and context.makeCurrent()) the first time a customer calls static API on a thread (or when there's no valid Scopes available on that thread yet). For the Java SDK we opted to customize ContextStorage to hand back a customized OTel Scope that restores the previous Context regardless of inner Scope instances not being cleaned up properly. You can find more details in the Java PR.
Hook
In order to fork our scopes, when required by OTel, we need some sort of a hook. We're not yet completely sure, when forking is actually required. In theory it should suffice to fork scopes, whenever a new OTel span is created, or maybe even only when the span is saved. What hooks are available in OTel depends on the language, so this will likely differer from SDK to SDK.
- Context Forking: Whenever a modified copy of an OTel
Contextis created usingcontext.with(...). - Context Storing: Whenever an OTel
Contextis stored usingcontext.makeCurrent() - Span Creation: Whenever a new OTel span is created, regardless of it being stored in any
Contextor thatContextbeing stored.
For Context forking / storing we could filter changes to only fork scopes when the span changes in order to have fewer forked scopes.
If no hook is available, we have to fall back to a more complex variant of global storage. See the middle example in this miro board.
A Context fork/storage hook alone unfortunately does not allow us to do everything we need. In SpanProcessor.onEnd and by extension also SpanExporter.export, Context.current() returns the parent Context and not the Context that was active during span execution. This seems to be by design in OTel. This means even if we managed to add our Scopes to Context, we can't access it in SpanProcessor.onEnd().
Storing Scopes which Belong to a Certain Span
If your language allows you to modify the OTel span and add Sentry Scopes to the span, that's probably the easiest way of getting scopes into SpanProcessor.onEnd and by extension SpanExporter.export. However we haven't explored this variant in detail yet.
If modifying the span isn't possible, the only way to retrieve the Scopes in SpanExporter.export, we've found so far, is to use a global storage. For this global storage, we use OTel spans as weakly referenced keys and Sentry Scopes as values. We use weak references, so we don't cause memory leaks, e.g. in case a span is never finished.
The hook for OTel span creation / Context forking / storing then needs to look up Sentry Scopes in either the span (if the language supports this variant) or the global storage.
Scopes forked in SpanProcessor.onStart can be found via the OTel span in Context (or global storage if span can't be modified). However, there may already be a Scopes object on the Context. The hook has to figure out which Scopes object to fork. An ancestry check can be used to see if the Scopes from Context is an ancestor of the Scopes of the span (or from global storage). If so, we fork the Scopes from the span (or global storage), since it's the "youngest". If that's not the case, we fork Scopes from Context or fall back to forking root scopes, if there's no Scopes on the Context.
We can't rely on Context.current() in SpanProcessor.onEnd as it will either return the parent Context or an unrelated Context. In SpanExporter.export we also can't use Context.current() because that's usually batched and may run on a different thread where Context isn't even propagated to.
Some of the variants for storing Scopes can be seen on this miro board. The variant on the right is preferred, if the SDK can modify spans in SpanProcessor.onStart. The variant in the middle is a fallback, if there's no hooks available. The variant on the left is what we use, when there's hooks but we can't modify spans in SpanProcessor.onStart.
Sentry API that interacts with OTel
Some of the Sentry API will have to create and manage modified copies of OTel Context. In withScope for example, we create a copy of the current Context and set forked Scopes on it using ctx = Context.current().with(forkedScopes). We then invoke the callback passed to withScope and afterwards restore previous Context, e.g. by calling .close() on a lifecycle management object handed to us by OTel.
When to fork Isolation Scope
Untested:
We can use Propagator.extract to fork isolation scope. We try to read the Scopes from the Context that's passed into Propagator.extract and fork that or fall back to forking root scopes if there's no Scopes in the Context.
Propagator.extract should be called by auto instrumentation for server and consumer use cases.
[If forking in Propagator.extract doesn't work out, we can try and check if a span has a parent in the current process (span.isRemote) and create an isolation scope if not.]
Tracing
See this Miro Board to learn how auto instrumentation, OpenTelemetry API and Sentry API play together in terms of incoming and outgoing tracing.
IDs
- We couldn't find a way to force certain span IDs to be used by OpenTelemetry, only trace ID was possible.
- When sending spans to Sentry we should keep the same span and trace ID used by OpenTelemetry and not accidentally create new ones which could render the trace useless.
Tracing Without Performance
Untested:
In Propagator.extract we can create PropagationContext from incoming headers (or similar metadata) or fall back to creating a new PropagationContext with random IDs. We then store this PropagationContet on the isolation scope. In Propagator.inject and when sending events to Sentry, we can use that PropagationContext from isolation scope and generate headers (or similar).
- tbd: how does freezing DSC/baggage work? Can we simply freeze whenever the first request (or similar) goes out?
- tbd: should Sentry.continueTrace write to isolation scope? Would it then also need to always fork an isolation scope at the same time? Should it create a new span (in case performance is enabled)?
Problems with this approach:
- Not all requests go through Propagator
extractandinject. See Miro Board. It's usually only those that are coming from OpenTelemetry auto instrumentation and it's not easily possible to use the OpenTelemetry SDK in a way whereextractandinjectare used for manual instrumentation.
Where to Store Sentry Span
Until we can completely remove Sentry Span and solely rely on OTel spans, we can store Sentry spans on the current scope. Storing it on the isolation scope would allow users to hide the current span by setting a span on the current scope, thereby breaking instrumentation. We'd have to modify isolation scope a lot to maintain which span is currently active - this would imply that the current span is leaked into e.g. async execution where there could be a separate span.
What to Move Along When Execution moves e.g. to Another Thread
When execution moves e.g. to another thread, we should bring along isolation scope and current scope. It may also make sense to have current scope forked in this case. If we're able to rely on OTels Context propagation, this should automatically be taken care of. See the right side of this miro board for examples.
What does Sentry Performance API look like?
tbd. There's no final decision on this matter yet. See DACI
Span status
Span status can be set on the OpenTelemetry span by serializing it into the description String of setStatus(StatusCode statusCode, String description) and then deserializing it when sending to Sentry or when Sentry span API is invoked.
Usage of OpenTelemetry span attributes
Since we're storing some internal information in OpenTelemetry span attributes (e.g. sampling decision, baggage, remote flag, ...), we should remove these internal attributes before sending the span to Sentry.
Sampling
We should try to configure a sampler in the OpenTelemetry SDK and use Sentry configuration for sampling in there. This sampling decision can then be copied when sending the spans to Sentry. We should not sample again when sending but just rely on the previous decision. The sampling decision can also be copied onto the span wrapper in case the Sentry SDKs implementation makes use of such a wrapper instead of handing back OpenTelemetry spans from Sentry API directly.
The OpenTelemetry sampler should also be used to filter out OpenTelemetry spans created for internal Sentry requests. This avoids spamming when customers are also using OTLP for exporting (which are not affected by what we send to Sentry in SpanExporter).
There are three kinds of OpenTelemetry sampling decision:
- RECORD_AND_SAMPLE: Goes through
SpanProcessorandSpanExporter - RECORD_ONLY: Only goes through
SpanProcessorbut not intoSpanExporter - DROP: Does NOT go into
SpanProcessororSpanExporter
To support Sentry API like custom sampling context, we still make the sampling decision for startTransaction in Scopes (used to be Hub) and then serialize it into separate OpenTelemetry span attributes (sampled, sample_rate, ...) when creating the OpenTelemetry span. The sampler we condigured for the OpenTelemetry SDK then makes use of these serialized attributes and reconstructs the sampling decision. We did it this way because we couldn't find a way to transfer the custom sampling context into the OpenTelemetry sampler without some kind of global storage.
Supporting the Sentry SDK with and without OpenTelemetry
In case it makes sense for an SDK to keep supporting previous instrumentation or an SDK cannot fully migrate to OpenTelemetry (yet), here's some things we did in those SDKs you might want to consider:
- Storage of
Scopes(used to beHub) should be made configurable to use OpenTelemetry if available or use the previous way of storing otherwise (e.g.ThreadLocal). - Performance API should be configurable as to whether it creates Sentry or OpenTelemetry spans under the hood.
- NOTE: Be careful, when using Sentry API in
SpanExporterto not create a loop and instead force usage of Sentry spans for this.
- NOTE: Be careful, when using Sentry API in
- To avoid duplicate spans when using both OpenTelemetry and previous Sentry instrumentation, we've added an
ignoredSpanOriginsoption which we pre-configure in OpenTelemetry mode to ignore spans coming from certain integrations we know would be duplicates.- Since Performance instrumentation and other Sentry feaures, like Errors, CRONS etc. are sometimes closely tied together into a single integration, this was the easiest way to allow opt-out of certain spans without creating tons of opt-out flags.
- Sentry
Transactionin OpenTelemetry mode is like a proxy that forwards to the root span which is only there to keep supporting previous API